
[Study stream live] New Course! Programming Abstractions in C++, Stanford CS106B, Part 1 YouTube
Programming methodology or equivalent; Students coming to CS106B are expected to have substantial prior experience with programming constructs such as loops, functions/methods, arrays, console and file I/O, standard data types (integer, string, and floating point), and classes. Students coming to CS106B are expected to know how to write code.

Abstraction in C++ Guide to Types of Abstraction with Examples
CS 106B: Programming Abstractions solving big(ger) problems and processing big(ger) data learning to manage complex data structures algorithmic analysis and algorithmic techniques such as recursion programming style and software development practices familiarity with the C++ programming language Prerequisite: CS 106A or equivalent

3. Object Oriented Programming Abstraction, Encapsulation, Inheritance, Polymorphism in C++
CS43: Functional Programming Abstractions, which introduces students to the functional programming paradigm using a popular programming language called Haskell. It's slightly more theoretical than CS106X and CS41, but it's been taught three times now and it's been very well received.. This just in from fellow Stanford classmate, Eunice Yang:

Powerful Abstractions for Programming Your Training Data · Stanford DAWN
Abstraction and its relation to programming. Software engineering principles of data abstraction and modularity. Object-oriented programming, fundamental data structures (such as stacks, queues, sets) and data-directed design. Recursion and recursive data structures (linked lists, trees, graphs). Introduction to time and space complexity analysis.

A Beginners Guide To Abstraction in ObjectOriented Programming
This course is the natural successor to Programming Methodology and covers such advanced programming topics as recursion, algorithmic analysis, and data abstraction using the C++ programming language, which is similar to both C and Java. If you've taken the Computer Science AP exam and done well (scored 4 or 5) or earned a good grade in a college course, Programming Abstractions may be an.

CS106B Programming Abstractions in C++ exercise 1.3 Gaussian Sum YouTube
out a little bit of the C++ language before we're done. Let me tell you about CS106. CS106 is the introductory programming sequence here at Stanford. It's our version of CS1, where you start at the beginning when you are interested in learning more about programming. We have a two-quarter sequence, A and B, that kind of follow together.
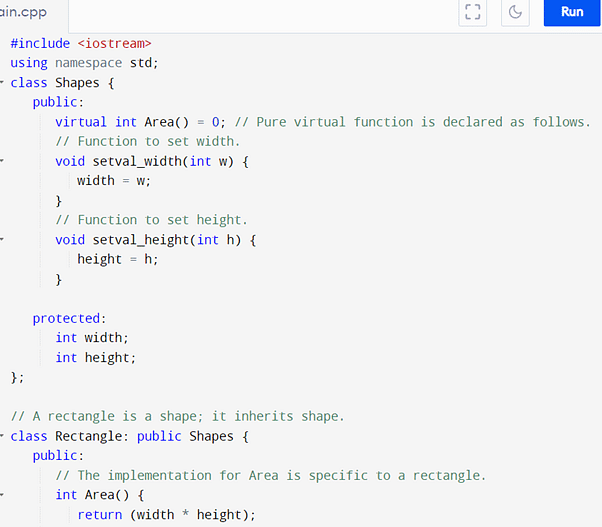
Understanding Abstract Class in C++ With Example Code
Programming Abstractions in C++. ISBN 978-0133454840. You can find different options to access the textbook here. Recommended readings for each lecture will be posted on our lecture schedule. Software. The official CS106 programming environment is Qt Creator, which is an editor bundled with C++ compiler and libraries. The software runs on.
GitHub khenderson20/stanfordprogrammingabstractionscpp exercises done on my own from the
8.4 Implementing the stack abstraction 8.5 Defining a scanner ADT Chapter 9. Efficiency and ADTs 9.1 The concept of an editor buffer 9.2 Defining the buffer abstraction 9.3 Implementing the editor using arrays 9.4 Implementing the editor using stacks 9.5 Implementing the editor using linked lists Chapter 10.
PPT CS 106X Programming Abstractions in C++ PowerPoint Presentation ID1983144
Textbook. Our textbook for CS106B this quarter is the following: Roberts, Eric S. Programming Abstractions in C++.ISBN 978-0133454840. Purchasing: Students can purchase the textbook from the Stanford University Bookstore, which is our recommended place to purchase this textbook.
CS 106B Programming Abstractions in C++ Working at Home
The first programming assignment of the quarter, Assignment 1: Welcome to C++!, goes out today. It's due on Friday, January 18th at the start of class (11:30AM). This assignment explores general C++ coding, strings, recursion, debugging, and the Stanford libraries. We hope you have fun with this one!

【Lecture 05】CS106B, Programming Abstractions in C++, Win 2018 YouTube
Abstraction and its relation to programming. Software engineering principles of data abstraction and modularity. Object-oriented programming, fundamental data structures (such as stacks, queues, sets) and data-directed design. Recursion and recursive data structures (linked lists, trees, graphs). Introduction to time and space complexity analysis.

GitHub khenderson20/stanfordprogrammingabstractionscpp exercises done on my own from the
Stanford CS106B. Contribute to heavy3/programming-abstractions development by creating an account on GitHub.

Roberts, Programming Abstractions in C A Second Course in Computer Science Pearson
Programming Abstractions in C++ Pearson, 2014 ISBN: 978-0133454840. C++ 1.1 Your first C++ program 1.2 The history of C++ 1.3 The compilation process 1.4 The structure of a C++ program 1.5 Variables 1.6 Data types 1.7 Expressions 1.8 Statements. 2.9 Introduction to the Stanford libraries 3 Strings 3.1 Using strings as abstract values.

CS106X Programming Abstractions in C++
The textbook used for the Stanford CS106B course is Roberts, Eric S. Programming Abstractions in C++, ISBN 978-0133454840. The book was written by Stanford CS professor Eric Roberts and targeted directly for CS106B. Readings from the textbook are suggested to accompany lecture.

PPT CS 106X Programming Abstractions in C++ PowerPoint Presentation ID1886605
Optional lab: CS106B is a course in programming abstractions and although we use C++, there is much more to the language that fits with our pedagogical goals. CS106L is a 1-unit S/NC lab designed to accompany CS106B/X and provide additional coverage of advanced features of the C++ language and standard libraries. It meets MW 4:15-5:05pm in.

斯坦福 抽象编程 (CS106B, Programming Abstractions in C++, Marty Stepp, Win 2018)【英】_哔哩哔哩 (゜゜)つロ 干杯
Lecture 3 by Julie Zelenski for the Programming Abstractions Course (CS106B) in the Stanford Computer Science Department. Julie goes over C++ libraries and e.